3-4 point distant low approach, one-space low pincer
Suppose 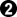 plays a pincer. White has prepared for that -
plays a pincer. White has prepared for that -  is played to have a good option towards the corner in this case. Nevertheless, if Black wants to build influence towards the upper side,
is played to have a good option towards the corner in this case. Nevertheless, if Black wants to build influence towards the upper side, 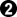 is a very good option.[1]
is a very good option.[1]
There are a few cases (3-4 point distant low approach, one-space low pincer, tenuki) of White playing tenuki after 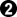 .
.
The order of 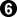 and
and  in the previous diagram is important. If Black plays the atari at
in the previous diagram is important. If Black plays the atari at  here first, White has the option of answering
here first, White has the option of answering  with the counteratari at
with the counteratari at  and capture
and capture  . Usually this is better for White than the joseki. If Black
chooses the correct line of play, White has no alternative.
. Usually this is better for White than the joseki. If Black
chooses the correct line of play, White has no alternative.
xela writing in early 2024: This is another urban myth that AI has dispelled. Even before AI, there's a small number of pro games on record with this "wrong" move order. And what happens? White just plays  at
at 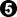 and it transposes into the usual joseki. The order doesn't matter. Asking KataGo (with star points in the other corners),
and it transposes into the usual joseki. The order doesn't matter. Asking KataGo (with star points in the other corners),  in this diagram and
in this diagram and  at
at 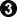 as per the usual joseki are equally good and should give the same result with best play. The
as per the usual joseki are equally good and should give the same result with best play. The 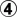 shown here is a small mistake. The difference is small enough that you could maybe call this an alternative joseki, but you can't really call it a mistake by black.
shown here is a small mistake. The difference is small enough that you could maybe call this an alternative joseki, but you can't really call it a mistake by black.
The standard variation continues with  here. Up to
here. Up to 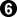 , White gets a solid group and Black builds thickness.
, White gets a solid group and Black builds thickness.  can be played at a instead, but that does leave bad aji and is now infrequent in pro games.
can be played at a instead, but that does leave bad aji and is now infrequent in pro games.
SnotNose Here is another possibility, though I'm not sure what the proper continuation is.
The purpose of  is to induce
is to induce  , making
, making  natural. It looks like white has bad aji here unless he plays at or around a next. Perhaps I haven't got
natural. It looks like white has bad aji here unless he plays at or around a next. Perhaps I haven't got  quite right (???).
quite right (???).
Charles From the point of view of basic suji,  is the previous diagram is worse than
is the previous diagram is worse than  here, in reply to
here, in reply to  .
.
SnotNose It still seems that white has bad aji at a and, so, may need a protective move at or around b or c at some point.
Charles This is the most usual finish to the joseki.
One should consider that  (of the Yup diagram) will probably be played, anyway.
(of the Yup diagram) will probably be played, anyway.
Having written that, I then found that the first diagram line is known in pro games - even recently - when White wants to push on up into the centre. So, it could be joseki, too: but less common.
Playing  instead of
instead of  looks logical, but in the sequence to
looks logical, but in the sequence to  , White collapses. After
, White collapses. After  , killing the corner with a and attacking in the center with b are miai for Black.
, killing the corner with a and attacking in the center with b are miai for Black.
If White is willing to give something up in the corner, so as notto be enclosed, she can play at  . Black can exchange Black a for White b in sente, but usually he will not do so, because the marked stone still has a lot of aji (Black b creates a ko, for example). More usually, Black either plays tenuki or pushes up with
. Black can exchange Black a for White b in sente, but usually he will not do so, because the marked stone still has a lot of aji (Black b creates a ko, for example). More usually, Black either plays tenuki or pushes up with 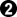 .
.
Alternatively, White can play at 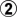 instead of
instead of 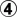 . Pressing against the black stone in the corner, she strengthens it, but also strengthens her own stones. After
. Pressing against the black stone in the corner, she strengthens it, but also strengthens her own stones. After  , the joseki continues with White a or b. Compared to the previous joseki, we get a reversal, with White facing the top and Black the left side.
, the joseki continues with White a or b. Compared to the previous joseki, we get a reversal, with White facing the top and Black the left side.
Black can also play 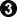 here. Black now takes the corner, giving White the outside.
here. Black now takes the corner, giving White the outside.
White can also cut, with 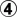 at
at 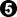 : this leads to a transposition to the joseki above.
: this leads to a transposition to the joseki above.
[1] An example is at enclosure opening distant low approach, pincer.
![[Diagram]](diagrams/6/eb6c6bed71a40c4dfdac8048037f399b.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/4/882d60c11996b8ea88639a91bc03db71.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/3/53076212e3660bcd74aff3d7c69c7cdf.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/30/fe08953d342e845b4d85bf4eae996496.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/4/a54f8c3b89dd4a5c339c5339305d85bb.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/1/f5e027c59bc6ef8ed4d8d3288f78b329.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/36/737e09c29fb5a2ab9b8197f3e6baf4cd.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/36/de5f987a7a720e50df803090532bde86.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/40/1e4a058a4575ad7196d6e0de22e51c7d.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/33/02f773d2d782c88590fd42b9b042c8a4.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/39/a7cdf089d5f2fdf4a713ff879f93deb9.png)
![[Diagram]](diagrams/28/f3d2d62f68c6237cd728e1edaf2e815c.png)
![Sensei's Library [Welcome to Sensei's Library!]](images/stone-hello.png)